An SSL certificate (also known as a public key certificate or digital certificate) is a file that proves ownership of a website’s public key and establishes a secure, encrypted connection between a web server and a web browser. A browser or application based on the encrypted TLS protocol.
All legitimate websites require an SSL certificate to verify ownership and increase the security of data packets traveling over the Internet. SSL is based on the latest encryption methods to ensure that hackers cannot create fake websites or steal user information.
SSL certificates often contain details about the issuer of the certificate, such as:
- Register the domain name for the certificate.
- The individual, organization, or device requesting the certificate.
- The certificate authority name.
- The signature of the certificate authority.
- Associated subdomains.
- Certificate issue date.
- Certificate expiration date.
- Public key (private key kept secret).
Basically, public and private keys are just long strings of characters used to encrypt and sign data. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key.
What are the different types of SSL certificates?
SSL certificate validation is the process by which a certificate authority (CA) verifies an individual’s or organization’s ownership and control of the domain for which they enroll a certificate. SSL only. Each different type of credential has a different level of credential verification, from minimal verification to thorough background checks. However, an SSL certificate of any authentication level provides the same level of TLS encryption, the only difference being how thoroughly the CA verifies the identity.
Based on the level of authentication, SSL certificates are divided into main types:
EV SSL – Extended Validation Certificate
Extended Validation (EV) certificates are the most advanced certificate type, and also the most expensive. EV SSL is often used on well-known websites with data collection and online payment functions. Websites using this certificate will typically display a “closed padlock, https, company name, and country” icon in the browser’s address bar. Displays information about the website owner in the address bar, making it easier for users to distinguish it from malicious domains.
In order to obtain an EV SSL certificate, website owners must go through a standardized identity verification process to confirm that they have legally acquired exclusive rights to the domain.
OV SSL – Organization Validation Certificate
Organization Validated certificates (OV) have a similar level of security and are the second most expensive certificates after EV SSL certificates. The purpose of OV SSL is to encrypt important personal information when users conduct transactions on the Internet. Therefore, commercial or publicly traded websites must install OV-SSL certificates to ensure that all information shared by customers is safe. OV SSL helps distinguish legitimate websites from otherwise malicious websites by displaying domain owner information. In order to obtain this certificate, website owners must also go through a verification process, which is not easy.
DV SSL – Domain Validation Certificate
A Domain Validated Certificate (DV) is one of the cheapest and easiest website security certificates to buy. DV SSL certificates have a less difficult verification process and therefore have the lowest level of encryption and less security. Typically used for blogs or informational sites unrelated to data collection or online transactions. The browser will only display the “lock, https” symbol in the address bar instead of the company name. Therefore, website owners can obtain such certificates simply by replying to an email or making a phone call to prove domain ownership.
Differentiate SSL certificates – Single Domain, Multi-Domain & Wildcard
Single domain name SSL certificate
A single-domain SSL certificate is an SSL certificate that secures a single domain name. That is, it will only work correctly if set on “www.example.com”. This is not the case for “abc.example.com” or any other variation.
A single-domain SSL certificate is the most affordable option for websites that are simple and straightforward, including most B2B or eCommerce sites where all transactions are under the same name. field.
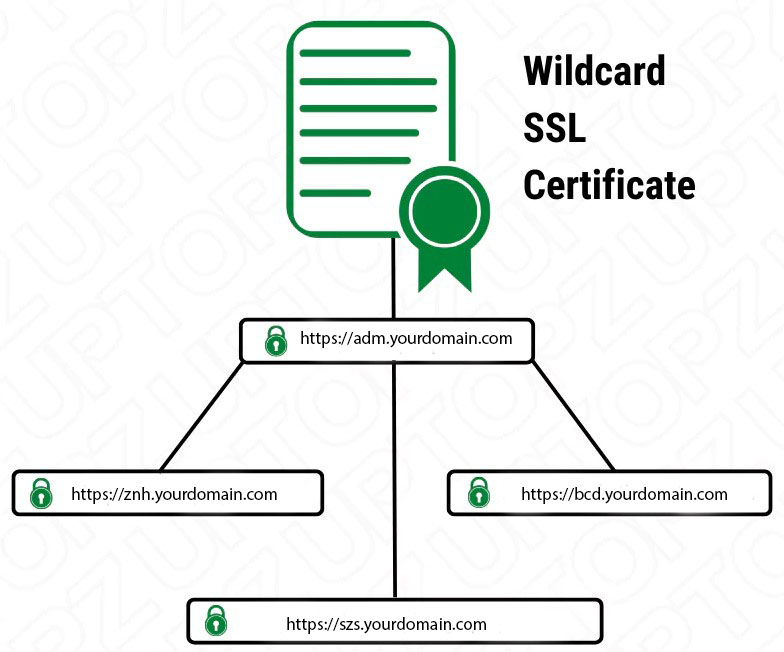
Wildcard SSL Certificate
Wildcard SSL certificates allow owners to secure unlimited main and subdomains on the same certificate. If you have multiple subdomains that require security, a single wildcard SSL certificate is more cost-effective than purchasing multiple separate SSL certificates.
Wildcard SSL certificates have an asterisk (*) as part of the common name. An asterisk also represents a subdomain with the same effective base domain.
Example: A wildcard SSL certificate protects the main domain example.com and other subdomains, including:
adm.yourdomain.com
bcd.yourdomain.com
szs.yourdomain.com
znh.yourdomain.com
Multi-Domain SSL Certificate ( MDC )
A Multi-Domain SSL Certificate (MDC) can be used to secure multiple domains or subdomains. It contains a combination of unique domains and subdomains with different TLDs (top-level domains) but no local/internal domains.
For example. :
yourdomain.com
yourdomain.net
yourdomain.au
yourdomain.uk
yourdomain.org
By default, this multi-domain certificate does not support subdomains. If you need to secure this default subdomain, you must provide both hostnames when retrieving the certificate.
Why use an SSL certificate?
SSL/TLS is currently the world’s leading website security standard. Every website needs an SSL certificate to verify ownership and protect user information from hackers. Although users won’t notice the difference between a website with or without SSL, most current browsers attempt to warn users of unsafe visits in a variety of ways that are visible to the user. Use of HTTP sites or invalid SSL certificate settings. Therefore, websites with valid SSL certificates are generally trusted by users and are more likely to rank in search engines.
Encryption: SSL certificates make it easier for clients to obtain the public key needed to open a TLS connection to a web server. A TLS connection is a secure connection using public and private keys, with each key pair used only in a single transaction, to ensure user privacy, server security, and the integrity of transmitted data.
Authentication: The SSL certificate confirms that the client is communicating with the correct server owning the domain. This helps prevent third-party domain spoofing attacks.
HTTPS: Set up an SSL certificate to transmit data via the secure HTTPS protocol. The two technologies go hand in hand, and you can’t use either. HTTPS Creates an HTTP connection secured by an SSL certificate.
Where you can buy an SSL certificate?
Every domain must receive a valid SSL certificate from a trusted CA certificate authority. CA Certificate Authority is also sometimes referred to as Certificates of Authority. Its main purpose is to authenticate entities (such as companies, organizations, individuals, websites, email addresses, etc.) and issue SSL certificates.
You can now buy cheap Domain Validated (DV) SSL certificates from the world’s leading providers:
ComodoSSLStore.com
Namecheap.com – Click to buy Namecheap SSL for only $3/year
GoDaddy.com – Get Godaddy SSL coupon
SSLs.com – Click to get SSL from $4.99
ssl2buy.com
Thank you readers for taking the time to read this article. Please visit the TopHostCoupon website for more useful information. See you in the next interesting article!